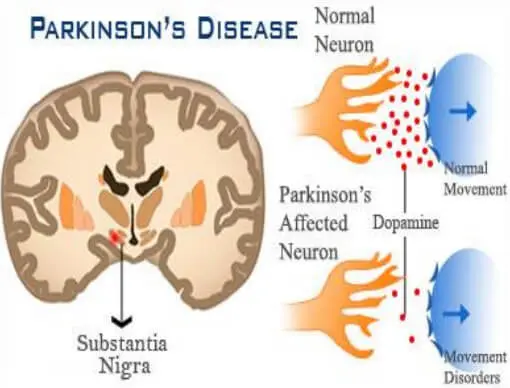
Parkinson's disease is a chronic and progressive degenerative disease of the central nervous system that is mainly caused by the lesion or death of neurons in the brain, resulting in abnormal dopamine secretion and reception.
Mask face: Lack of facial expression
Tremor: It usually starts with one side of the limb and shakes quite a lot when the limb is not moving.
Writing becomes smaller: Writing fonts become smaller and smaller stiffness in the limbs stiffness in the limbs, inflexible movement, easy muscle and joint pain
Hypotension: Dizziness with postural hypotension
Inadequate muscle tension: Continuous muscle contraction, resulting in involuntary twisting of the limb
Vague speech: Talking is getting smaller and smaller
Unsteady and unstable gait: Symptoms progress from unilateral to bilateral extremities, with slower movement, as if stuck to the floor and dragging, and then almost impossible to stride, only walking in small steps
Abnormal sensory function: Including numbness of the limbs, lack of smell incontinence will appear frequent urination, sexual dysfunction and other autonomic disorders
Hunchback: Walking weight will shift forward, the body hunchback easy to fall
Delayed movement: Slow body movements
Drugs: such as dopamine inhibitors, MAO-B nhibitors, OMT inhibitors, levodopa, anticholinergics, Amantadine, etc. COMT inhibitors, levodopa, anticholinergic agents, Amantadine, etc.
Surgery: Such as pale bulb cautery, deep brain stimulation, etc.
Non-pharmacological treatments: Education, nutrition, exercise, physical rehabilitation, speech therapy, etc.
Stem cell therapy: The use of stem cell regeneration and repair to treat Parkinson's disease is the latest treatment modality.